|
|
| (21 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) |
| Line 9: |
Line 9: |
| |-| Using YAML with yq = | | |-| Using YAML with yq = |
| <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> |
| openstack image list -f yaml | yq '[ .[] | select(.Name != null) | select(.Name | match("(?i)kubernetes")) ]' | | openstack image list --format yaml | yq '[ .[] | select(.Name != null) | select(.Name | match("(?i)kubernetes")) ]' |
| </syntaxhighlight> | | </syntaxhighlight> |
|
| |
|
| Line 26: |
Line 26: |
| |-| Using JSON with jq = | | |-| Using JSON with jq = |
| <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> |
| openstack image list -f json | jq '[ .[] | select(.Name | . != null and match("(?i)kubernetes")) ]' | | openstack image list --format json | jq '[ .[] | select(.Name | . != null and match("(?i)kubernetes")) ]' |
| </syntaxhighlight> | | </syntaxhighlight> |
|
| |
|
| Line 49: |
Line 49: |
| ] | | ] |
| </syntaxhighlight> | | </syntaxhighlight> |
| | </tabber> |
| | |
| | = Node groups = |
| | Node groups are used to create Kubernetes nodes with different properties (for example flavors). |
| | |
| | When creating a cluster, the following two node groups are created by default (see <code>openstack coe nodegroup list</code>): |
| | <syntaxhighlight lang="text"> |
| | +--------------------------------------+----------------+-----------------------------+--------------------------------------+------------+-----------------+--------+ |
| | | uuid | name | flavor_id | image_id | node_count | status | role | |
| | +--------------------------------------+----------------+-----------------------------+--------------------------------------+------------+-----------------+--------+ |
| | | 5914ba24-99e5-4adf-b1a7-f53f8872d001 | default-master | Standard Düdingen c002m0004 | aa1eb1ec-c358-4bd6-a606-5272de053484 | 1 | CREATE_COMPLETE | master | |
| | | 93e2c2c4-e4b1-4874-ad64-2b832868ff10 | default-worker | Standard Düdingen c002m0004 | aa1eb1ec-c358-4bd6-a606-5272de053484 | 1 | CREATE_COMPLETE | worker | |
| | +--------------------------------------+----------------+-----------------------------+--------------------------------------+------------+-----------------+--------+ |
| | </syntaxhighlight> |
| | |
| | Notes: |
| | * The node group <code>default-master</code> is used for Kubernetes control plane nodes. |
| | * The node group <code>default-worker</code> is used for Kubernetes worker nodes. |
| | |
| | = Authentication with application credentials = |
| | When interacting with the OpenStack API, be it via CLI or through Terraform / OpenTofu, you have two possibilities for authentication: |
| | * Your username and password |
| | * Application credentials |
| | |
| | When using application credentials, it is important to use ones that have been configured with <code>Unrestricted=True</code>. |
| | <tabber> |
| | |-| OpenStack CLI = |
| | <syntaxhighlight lang='bash'> |
| | application_credential_name=opentofu |
| | |
| | openstack application credential create \ |
| | --unrestricted \ |
| | ${application_credential_name} |
| | </syntaxhighlight> |
| | |
| | Example output: |
| | <syntaxhighlight lang='text' highlight=9> |
| | +--------------+----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ |
| | | Field | Value | |
| | +--------------+----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ |
| | | id | 3db9f5b71b8f4dc4889c552feb188db3 | |
| | | name | opentofu | |
| | | description | None | |
| | | project_id | 51350793d7424136a058221a7530b675 | |
| | | roles | reader _member_ member | |
| | | unrestricted | True | |
| | | access_rules | [] | |
| | | expires_at | None | |
| | | secret | AGBBjyWgSgW4bZfsOdH8WjD-_OY55Szo3SLPqSht78OXsBbWSvTmPMz24_9gwodxTGSJ5-Lttz5mK8ZLoGMPOQ | |
| | +--------------+----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ |
| | </syntaxhighlight> |
| | |
| | |-| OpenStack dashboard = |
| | Navigate to <code>Identity -> Application Credentials</code>, then click the button <code>+Create Application Credential</code> in the upper right corner. |
| | |
| | [[File:Kubernetes management 001.png|1000px]] |
| | |
| | In the <code>Create Application Credential</code> mask, fill in the <code>Name</code> and make sure to check the <code>Unrestricted (dangerous)</code> check box. Then click the <code>Create Application Credential</code> button. |
| | |
| | [[File:Kubernetes management 002.png|1000px]] |
| | |
| | You will now be presented with a view of the newly created application credential. |
| | |
| | [[File:Kubernetes management 003.png|1000px]] |
| </tabber> | | </tabber> |
|
| |
|
| Line 55: |
Line 119: |
| Use <code>openstack coe cluster template create</code> to create a cluster template: | | Use <code>openstack coe cluster template create</code> to create a cluster template: |
| <tabber> | | <tabber> |
| |-| Command = | | |-| OpenStack CLI = |
| <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> |
| # ID or name of the OpenStack Kubernetes image to use: | | # ID or name of the OpenStack Kubernetes image to use: |
| Line 69: |
Line 133: |
| --master-flavor 'Standard Düdingen c002m0004' \ | | --master-flavor 'Standard Düdingen c002m0004' \ |
| --flavor 'Standard Düdingen c002m0004' \ | | --flavor 'Standard Düdingen c002m0004' \ |
| --public \
| |
| --master-lb-enabled | | --master-lb-enabled |
| </syntaxhighlight> | | </syntaxhighlight> |
| Line 113: |
Line 176: |
| </syntaxhighlight> | | </syntaxhighlight> |
| </tabber> | | </tabber> |
| | |
| | Please note that the argument <code>--external-network public</code> will use the default floating IP addresses. If you wish to use a different network, replace <code>public</code> accordingly. |
|
| |
|
| For a list of all labels see [https://docs.openstack.org/magnum/latest/user/#labels Magnum User Guide - Labels]. | | For a list of all labels see [https://docs.openstack.org/magnum/latest/user/#labels Magnum User Guide - Labels]. |
| Line 119: |
Line 184: |
| Use <code>openstack coe cluster create</code> to create a cluster: | | Use <code>openstack coe cluster create</code> to create a cluster: |
| <tabber> | | <tabber> |
| |-| Command = | | |-| OpenStack CLI = |
| <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> |
| # ID or name of the cluster template to use: | | # ID or name of the cluster template to use: |
| Line 132: |
Line 197: |
| --node-count 2 | | --node-count 2 |
| </syntaxhighlight> | | </syntaxhighlight> |
| |-| Example output =
| | |
| | Example output: |
| <syntaxhighlight lang="text"> | | <syntaxhighlight lang="text"> |
| Request to create cluster 9bb54949-2469-4b7e-99c8-4cb2730d4e8f accepted | | Request to create cluster 9bb54949-2469-4b7e-99c8-4cb2730d4e8f accepted |
| </syntaxhighlight> | | </syntaxhighlight> |
| </tabber>
| |
|
| |
|
| Options: | | Options: |
| * <code>--master-count</code>: number of control plane nodes. | | * <code>--master-count</code>: number of control plane nodes. Note that the number of control plane nodes must be odd due to etcd. Cluster creation will fail if the number of control plane nodes is even. |
| * <code>--node-count</code>: number of worker nodes. | | * <code>--node-count</code>: number of worker nodes. |
| | |-| OpenTofu/Terraform = |
| | <syntaxhighlight lang="tf"> |
| | data "openstack_containerinfra_clustertemplate_v1" "k8s_template_1_30" { |
| | name = "kubernetes-1.30.2" |
| | } |
|
| |
|
| After running <code>openstack coe cluster create</code>, you can inspect the cluster's state using <code>openstack coe cluster list</code> (it will take some time for the cluster to be created):
| | resource "openstack_containerinfra_cluster_v1" "cluster_1" { |
| | name = "cluster-1" |
| | cluster_template_id = data.openstack_containerinfra_clustertemplate_v1.k8s_template_1_30.id |
| | master_count = 1 |
| | node_count = 2 |
| | } |
| | </syntaxhighlight> |
| | </tabber> |
| | |
| | After creating the cluster, you can inspect the cluster's state using <code>openstack coe cluster list</code> (it will take some time for the cluster to be created): |
| <tabber> | | <tabber> |
| |-| Command = | | |-| OpenStack CLI = |
| <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> |
| openstack coe cluster list | | openstack coe cluster list |
| Line 204: |
Line 283: |
| </tabber> | | </tabber> |
|
| |
|
| = Management = | | = Scaling = |
| == Management - Control plane == | | == Scaling - Worker nodes == |
| TBD
| |
| | |
| == Management - Worker nodes ==
| |
| Use <code>openstack coe cluster resize</code> to change the number of worker nodes in a cluster: | | Use <code>openstack coe cluster resize</code> to change the number of worker nodes in a cluster: |
| <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> |
| Line 221: |
Line 297: |
|
| |
|
| = Upgrade = | | = Upgrade = |
| To upgrade a cluster (upgrading the version of Kubernetes), a new [[#Creation - Cluster template | cluster template needs to be created]] first. This cluster template must use a newer Kubernetes version than the one used in your current cluster template. Downgrades are also possible, but haven't been tested in detail. | | To upgrade a cluster (upgrading the version of Kubernetes), a new [[#Creation - Cluster template | cluster template needs to be created]] first. This cluster template must use a newer Kubernetes version than the one used in your current cluster template. |
|
| |
|
| After creating the cluster template, use <code>openstack coe cluster upgrade</code> to assign the new cluster template to your cluster: | | After creating the cluster template, use <code>openstack coe cluster upgrade</code> to assign the new cluster template to your cluster: |
| <tabber> | | <tabber> |
| |-| Command = | | |-| OpenStack CLI = |
| <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> |
| # ID or name of the cluster to upgrade: | | # ID or name of the cluster to upgrade: |
| Line 241: |
Line 317: |
| </tabber> | | </tabber> |
|
| |
|
| After running <code>openstack coe cluster upgrade</code>, you can inspect the cluster's state using <code>openstack coe cluster list</code> (it will take some time for the cluster upgrade to be completed): | | After running <code>openstack coe cluster upgrade</code>, you can inspect the cluster's state using <code>openstack coe cluster list</code> (it will take some time for the cluster upgrade/downgrade to be completed): |
| <tabber> | | <tabber> |
| |-| Command = | | |-| OpenStack CLI = |
| <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> |
| openstack coe cluster list | | openstack coe cluster list |
| Line 266: |
Line 342: |
| </syntaxhighlight> | | </syntaxhighlight> |
| </tabber> | | </tabber> |
| | |
| | = Downgrade = |
| | A downgrade of a cluster works the same as an [[#Upgrade | Upgrade]], but you will have to use a cluster template that uses an image with an older Kubernetes version. |
|
| |
|
| = Deletion = | | = Deletion = |
Overview
This page describes the creation and management of Kubernetes clusters in our OpenStack-based stoney cloud using the Magnum container orchestration engine (COE).
Note: This page is a work-in-progress, so if you face any challenges, please contact us with the specific issue.
Images
To list available Kubernetes images, use openstack image list with the following yq/jq filter:
openstack image list --format yaml | yq '[ .[] | select(.Name != null) | select(.Name | match("(?i)kubernetes")) ]'
Example output:
- ID: da535156-e7c8-461d-a0ed-03bcf878d5a6
Name: 'Ubuntu 22.04 (240702): Kubernetes v1.28.11'
Status: active
- ID: aa1eb1ec-c358-4bd6-a606-5272de053484
Name: 'Ubuntu 22.04 (240702): Kubernetes v1.29.6'
Status: active
- ID: db68e8e8-d4b4-4c4f-af41-4166eb33973d
Name: 'Ubuntu 22.04 (240702): Kubernetes v1.30.2'
Status: active
openstack image list --format json | jq '[ .[] | select(.Name | . != null and match("(?i)kubernetes")) ]'
Example output:
[
{
"ID": "da535156-e7c8-461d-a0ed-03bcf878d5a6",
"Name": "Ubuntu 22.04 (240702): Kubernetes v1.28.11",
"Status": "active"
},
{
"ID": "aa1eb1ec-c358-4bd6-a606-5272de053484",
"Name": "Ubuntu 22.04 (240702): Kubernetes v1.29.6",
"Status": "active"
},
{
"ID": "db68e8e8-d4b4-4c4f-af41-4166eb33973d",
"Name": "Ubuntu 22.04 (240702): Kubernetes v1.30.2",
"Status": "active"
}
]
Node groups
Node groups are used to create Kubernetes nodes with different properties (for example flavors).
When creating a cluster, the following two node groups are created by default (see openstack coe nodegroup list):
+--------------------------------------+----------------+-----------------------------+--------------------------------------+------------+-----------------+--------+
| uuid | name | flavor_id | image_id | node_count | status | role |
+--------------------------------------+----------------+-----------------------------+--------------------------------------+------------+-----------------+--------+
| 5914ba24-99e5-4adf-b1a7-f53f8872d001 | default-master | Standard Düdingen c002m0004 | aa1eb1ec-c358-4bd6-a606-5272de053484 | 1 | CREATE_COMPLETE | master |
| 93e2c2c4-e4b1-4874-ad64-2b832868ff10 | default-worker | Standard Düdingen c002m0004 | aa1eb1ec-c358-4bd6-a606-5272de053484 | 1 | CREATE_COMPLETE | worker |
+--------------------------------------+----------------+-----------------------------+--------------------------------------+------------+-----------------+--------+
Notes:
- The node group
default-master is used for Kubernetes control plane nodes.
- The node group
default-worker is used for Kubernetes worker nodes.
Authentication with application credentials
When interacting with the OpenStack API, be it via CLI or through Terraform / OpenTofu, you have two possibilities for authentication:
- Your username and password
- Application credentials
When using application credentials, it is important to use ones that have been configured with Unrestricted=True.
application_credential_name=opentofu
openstack application credential create \
--unrestricted \
${application_credential_name}
Example output:
+--------------+----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Field | Value |
+--------------+----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| id | 3db9f5b71b8f4dc4889c552feb188db3 |
| name | opentofu |
| description | None |
| project_id | 51350793d7424136a058221a7530b675 |
| roles | reader _member_ member |
| unrestricted | True |
| access_rules | [] |
| expires_at | None |
| secret | AGBBjyWgSgW4bZfsOdH8WjD-_OY55Szo3SLPqSht78OXsBbWSvTmPMz24_9gwodxTGSJ5-Lttz5mK8ZLoGMPOQ |
+--------------+----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
Navigate to Identity -> Application Credentials, then click the button +Create Application Credential in the upper right corner.
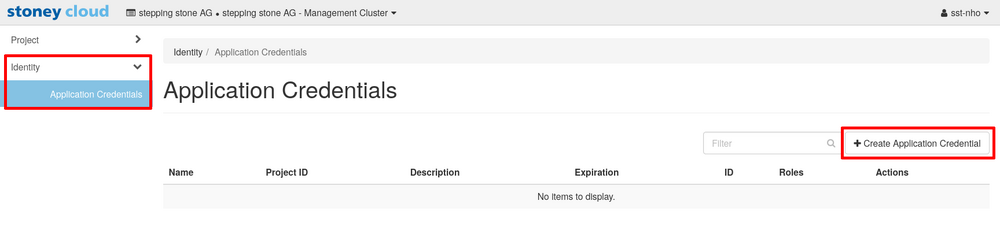
In the Create Application Credential mask, fill in the Name and make sure to check the Unrestricted (dangerous) check box. Then click the Create Application Credential button.
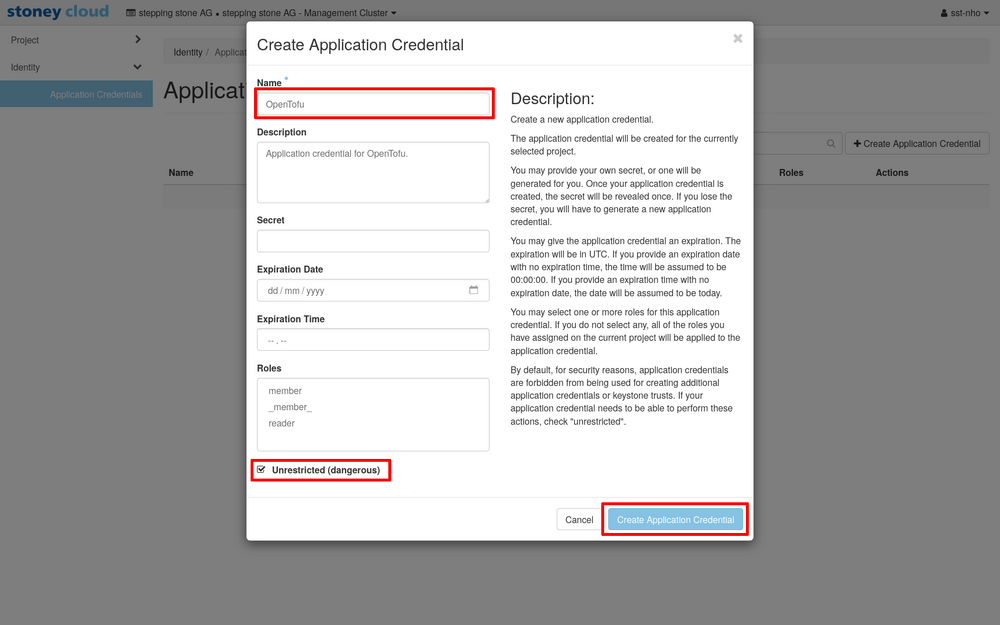
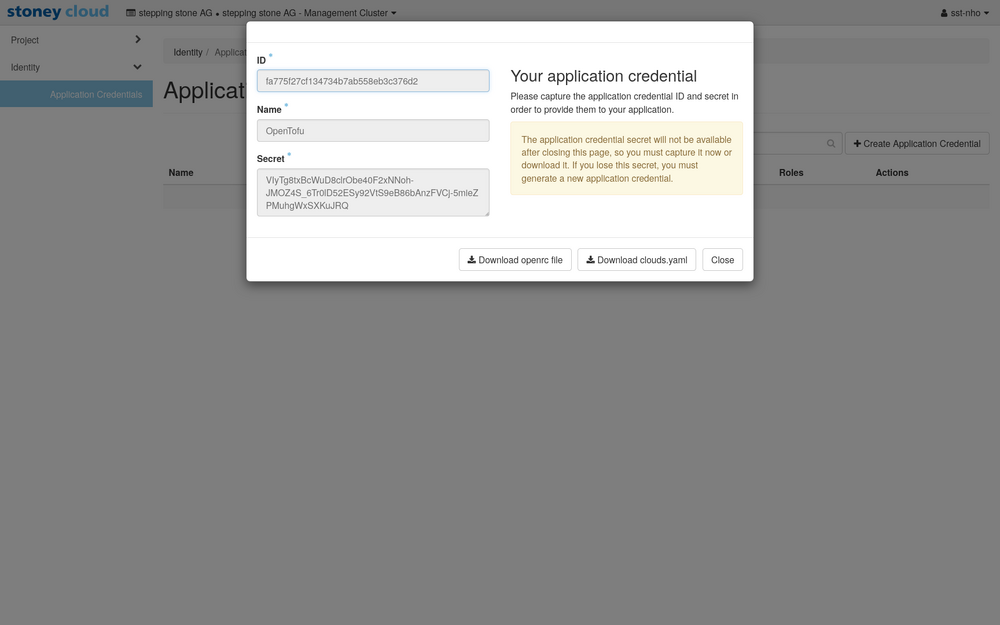
You will now be presented with a view of the newly created application credential.
Creation
Creation - Cluster template
Use openstack coe cluster template create to create a cluster template:
# ID or name of the OpenStack Kubernetes image to use:
image=c539d525-d912-4acb-a7c3-bfcaf5f533c5 # Ubuntu 22.04 (20240605): Kubernetes v1.30.1
# Name of the cluster template to create:
cluster_template=''
openstack coe cluster template create "$cluster_template" \
--coe kubernetes \
--image "$image" \
--external-network public \
--master-flavor 'Standard Düdingen c002m0004' \
--flavor 'Standard Düdingen c002m0004' \
--master-lb-enabled
Request to create cluster template kubernetes-1.30.2 accepted
+-----------------------+--------------------------------------+
| Field | Value |
+-----------------------+--------------------------------------+
| insecure_registry | - |
| labels | {} |
| updated_at | - |
| floating_ip_enabled | True |
| fixed_subnet | - |
| master_flavor_id | Standard Düdingen c002m0004 |
| uuid | d69969e7-1239-4810-b092-c758d3e9ef2e |
| no_proxy | - |
| https_proxy | - |
| tls_disabled | False |
| keypair_id | - |
| public | True |
| http_proxy | - |
| docker_volume_size | - |
| server_type | vm |
| external_network_id | public |
| cluster_distro | ubuntu |
| image_id | db68e8e8-d4b4-4c4f-af41-4166eb33973d |
| volume_driver | - |
| registry_enabled | False |
| docker_storage_driver | overlay2 |
| apiserver_port | - |
| name | kubernetes-1.30.2 |
| created_at | 2024-08-07T14:39:52.314174+00:00 |
| network_driver | flannel |
| fixed_network | - |
| coe | kubernetes |
| flavor_id | Standard Düdingen c002m0004 |
| master_lb_enabled | True |
| dns_nameserver | 8.8.8.8 |
| hidden | False |
| tags | - |
+-----------------------+--------------------------------------+
Please note that the argument --external-network public will use the default floating IP addresses. If you wish to use a different network, replace public accordingly.
For a list of all labels see Magnum User Guide - Labels.
Creation - Cluster
Use openstack coe cluster create to create a cluster:
# ID or name of the cluster template to use:
cluster_template=''
# Name of the cluster to create:
cluster=''
openstack coe cluster create "$cluster" \
--cluster-template "$cluster_template" \
--master-count 1 \
--node-count 2
Example output:
Request to create cluster 9bb54949-2469-4b7e-99c8-4cb2730d4e8f accepted
Options:
--master-count: number of control plane nodes. Note that the number of control plane nodes must be odd due to etcd. Cluster creation will fail if the number of control plane nodes is even.--node-count: number of worker nodes.
data "openstack_containerinfra_clustertemplate_v1" "k8s_template_1_30" {
name = "kubernetes-1.30.2"
}
resource "openstack_containerinfra_cluster_v1" "cluster_1" {
name = "cluster-1"
cluster_template_id = data.openstack_containerinfra_clustertemplate_v1.k8s_template_1_30.id
master_count = 1
node_count = 2
}
After creating the cluster, you can inspect the cluster's state using openstack coe cluster list (it will take some time for the cluster to be created):
openstack coe cluster list
Status during cluster creation:
+--------------------------------------+----------------+------------+------------+--------------+--------------------+---------------+
| uuid | name | keypair | node_count | master_count | status | health_status |
+--------------------------------------+----------------+------------+------------+--------------+--------------------+---------------+
| e41cc55c-9f63-4880-9c18-0c021545efa4 | sst-yde-test-1 | None | 1 | 1 | CREATE_IN_PROGRESS | None |
+--------------------------------------+----------------+------------+------------+--------------+--------------------+---------------+
Status after that the cluster has been successfully created:
+--------------------------------------+----------------+------------+------------+--------------+--------------------+---------------+
| uuid | name | keypair | node_count | master_count | status | health_status |
+--------------------------------------+----------------+------------+------------+--------------+--------------------+---------------+
| e41cc55c-9f63-4880-9c18-0c021545efa4 | sst-yde-test-1 | None | 1 | 1 | CREATE_COMPLETE | HEALTHY |
+--------------------------------------+----------------+------------+------------+--------------+--------------------+---------------+
Creation - Cluster - Access
To access a created cluster with kubectl, helm etc., use openstack coe cluster config to retrieve the cluster's configuration (essentially the "kubeconfig" file):
# ID or name of the cluster:
cluster=''
# Path to the directory where the Kubeconfig file will be stored:
directory="$HOME"/.kube
# Make sure the directory exists:
mkdir --parent "$directory"
# Download the kubeconfig.
# This will create the kubeconfig file at $directory/config
openstack coe cluster config --dir "$directory" "$cluster"
Depending on where the kubeconfig file has been store, you will need to set the environment variable KUBECONFIG accordingly (if you used the directory .kube in your home directory, this step is not required as ~/.kube/config is the default kubeconfig path):
export KUBECONFIG=/path/to/kube/config
You will now be able to access the cluster using kubectl:
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION INTERNAL-IP EXTERNAL-IP OS-IMAGE KERNEL-VERSION CONTAINER-RUNTIME
sst-yde-test-1-fj6ladv5sne3-control-plane-jl86d Ready control-plane 45m v1.28.11 10.0.0.149 <none> Ubuntu 22.04.4 LTS 5.15.0-113-generic containerd://1.7.13
sst-yde-test-1-fj6ladv5sne3-default-worker-b2c7j-5bh2w Ready <none> 44m v1.28.11 10.0.0.150 <none> Ubuntu 22.04.4 LTS 5.15.0-113-generic containerd://1.7.13
Scaling
Scaling - Worker nodes
Use openstack coe cluster resize to change the number of worker nodes in a cluster:
# ID or name of the cluster:
cluster=''
# Number of worker nodes:
nodes=''
openstack coe cluster resize "$cluster" "$nodes"
Upgrade
To upgrade a cluster (upgrading the version of Kubernetes), a new cluster template needs to be created first. This cluster template must use a newer Kubernetes version than the one used in your current cluster template.
After creating the cluster template, use openstack coe cluster upgrade to assign the new cluster template to your cluster:
# ID or name of the cluster to upgrade:
cluster=''
# ID or name of the new cluster template to use:
cluster_template=''
openstack coe cluster upgrade "$cluster" "$cluster_template"
Request to upgrade cluster sst-yde-test-1 has been accepted.
After running openstack coe cluster upgrade, you can inspect the cluster's state using openstack coe cluster list (it will take some time for the cluster upgrade/downgrade to be completed):
openstack coe cluster list
During the upgrade:
+--------------------------------------+----------------+------------+------------+--------------+--------------------+---------------+
| uuid | name | keypair | node_count | master_count | status | health_status |
+--------------------------------------+----------------+------------+------------+--------------+--------------------+---------------+
| e41cc55c-9f63-4880-9c18-0c021545efa4 | sst-yde-test-1 | None | 1 | 1 | UPDATE_IN_PROGRESS | UNHEALTHY |
+--------------------------------------+----------------+------------+------------+--------------+--------------------+---------------+
After the upgrade:
+--------------------------------------+----------------+------------+------------+--------------+-----------------+---------------+
| uuid | name | keypair | node_count | master_count | status | health_status |
+--------------------------------------+----------------+------------+------------+--------------+-----------------+---------------+
| e41cc55c-9f63-4880-9c18-0c021545efa4 | sst-yde-test-1 | None | 1 | 1 | UPDATE_COMPLETE | HEALTHY |
+--------------------------------------+----------------+------------+------------+--------------+-----------------+---------------+
Downgrade
A downgrade of a cluster works the same as an Upgrade, but you will have to use a cluster template that uses an image with an older Kubernetes version.
Deletion
Deletion - Cluster template
Use openstack coe cluster template delete to delete a cluster template:
# ID or name of the cluster template to delete:
cluster_template=''
openstack coe cluster template delete "$cluster_template"
Deletion - Cluster
Use openstack coe cluster delete to delete a cluster:
# ID or name of the cluster to delete:
cluster=''
openstack coe cluster delete "$cluster"
Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting - Adjusting the Kubernetes image label kube_version
When creating a cluster using openstack coe cluster create, you might encounter the following error:
Image c539d525-d912-4acb-a7c3-bfcaf5f533c5 does not have a kube_version property.
To fix this problem, add the kube_version property to the image:
# ID or name of the OpenStack Kubernetes image to adjust:
image_id=''
# The Kubernetes version of the image:
k8s_image_version=v1.30.1
# Adjust the image and add the "kube_version" property:
openstack image set "$image_id" --property kube_version="$k8s_image_version"
After adjust the image property you will have to delete the existing cluster and re-create it using openstack coe cluster create.


